NOTES
What is Garbage?
All the waste materials and other household waste produced on a daily basis are termed as garbage. The different wastes of garbage contain peels of vegetable and fruits, leftovers cooked food products, waste paper, and plastic materials, and many other waste items.
Waste
Waste is any substance, which is discarded after primary use, or it is worthless, defective and of no use.
Composting and Vermicomposting
Compost
- Compost is an organic matter that has been decomposed and recycled as a fertilizer and soil nutrient.
Vermicomposting
- Vermicompost (or vermicompost) is the product of the composting process using various species of worms.
- Red wigglers, White worms and other earthworms are used to create a mixture of decomposing vegetables or food waste, garden waste, farm waste etc
- The product, vermicompost, is excellent manure for gardens, nurseries, farms etc.
Exercise Questions
1. (a) Which kind of garbage is not converted into compost by the red worms?
(b) Have you seen any other organism besides red worms, in your pit? If yes, try to find out their names. Draw pictures of these.
Solution:
a) Pieces of cloth, polythene bags, broken glass, aluminium wrappers, nails and broken toys are not converted into compost by the red worms.
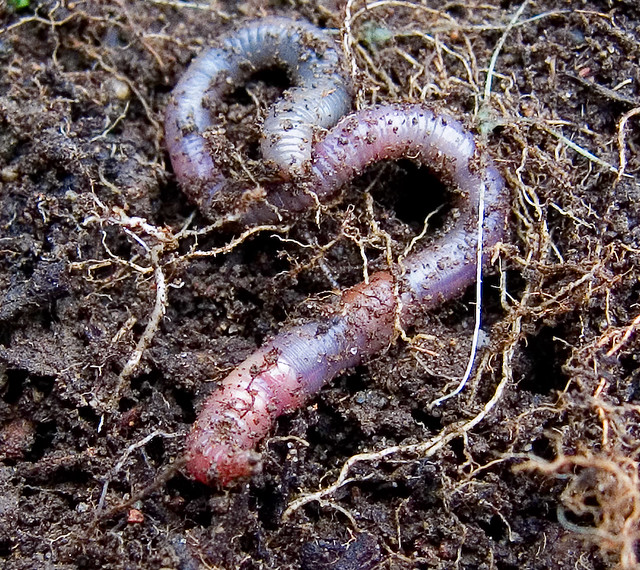
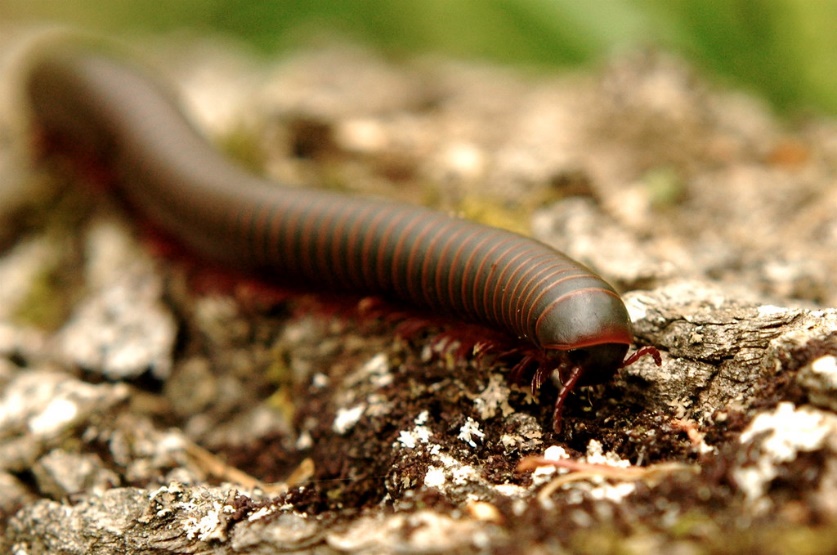
b) Earthworms, small insects like ant, millipedes are found in pits.



2. Discuss:
(a) Is garbage disposal the responsibility only of the government?
(b) Is it possible to reduce the problems relating to disposal of garbage?
Solution:
a) No, not just the government, but everybody is responsible for garbage disposal. We should bifurcate wet and dry waste, recycle the non-biodegradable substances and we should also reduce the accumulation of garbage in our house and streets.
b) Yes, it is possible to reduce the problems of garbage by scientific disposal of garbage, we can do it by bifurcation of different waste and also by recycling the waste materials.
3. (a) What do you do with the leftover food at home?
(b) If you and your friends are given the choice of eating in a plastic plate or a banana leaf platter at a party, which one would you prefer and why?
Solution:
(a) Leftover food can be collected and used to form compost. Compost produces nutrients necessary for the growth and development of plants.
(b) We would prefer to eat food on a banana leaf plate because it acts as a harmless substance which helps to form manure by the process of composting, whereas plastic plates cannot be converted into harmless substances by composting. Plastic plates are not degradable, hence can persist in the environment and cause many problems.
4. (a) Collect pieces of different kinds of paper. Find out which of these can be recycled.
(b) With the help of a lens look at the pieces of paper, you collected for the above question. Do you see any difference in the material of recycled paper and a new sheet of paper?
Solution:
(a) Papers such as newspapers, notebooks, magazines can be recycled easily. However, shiny and coated papers cannot be easily recycled
(b) Recycled paper is usually thick or rough when compared to a new sheet of paper.
5. (a)Collect different kinds of packaging material. What was the purpose for which each one was used? Discuss in groups.
(b) Give an example in which packaging could have been reduced?
(c) Write a story on how packaging increases the amount of garbage.
Solution:
(a) Different kinds of packaging materials used commonly are:
Cardboard – used as shoe, soap, bulb and other boxes.
Plastic Bags – Toys covers, sarees bags, shopping bags, etc.
Wooden Boxes – Fruit baskets and boxes for hardware.
Jute Bags – School bags, shopping bags, vegetable bags, etc.
(b) By reusing the packaging material, we can reduce the accumulation of garbage.
(c) The basic purpose of packaging is to protect the product from tampering and to maintain its freshness and purity. However, most of the packaging material is used to beautify the boxes and make them look attractive on the shelves. Unfortunately, a large volume of packaging material goes waste and is thrown into the dustbin.
For example, in most of the places, the dustbins are full of chips and biscuit wrappers.
It unnecessarily increases the amount of garbage. It also increases the cost of the product due to unnecessary packaging. We should seriously consider how to reduce unnecessary packaging.
6. Do you think it is better to use compost instead of chemical fertilizers? Why?
Solution:
Yes, it is better to use compost instead of chemical fertilizers for the following reasons:
- It is easy to prepare compost
- Compost is environment friendly as it does not cause any health issues in humans and animals
- Compost will not cause pollution
- Compost increases soil fertility.
- Compost is biodegradable.