NOTES
Source of light: An object which emits light, is called a source of light. For example, sun, torch, etc.
Non-luminous objects: These are the objects which do not emit light of their own. Such a body becomes visible when light falls on it. For example, the moon, the planets, etc.
Ray of light: A straight thin beam of light from a source to an object is called a ray of light.
Obstacle: An object which comes to the path of the light is called an obstacle.
Formation of a shadow
- All the opaque objects seem to form a dark shadow of their own.
- We need a source of light, an opaque object in the way, and a screen to see a shadow.
- Screen: This is a surface on which the shadow is formed. It may be a butter paper or simply ground.
- Shadows give us some information about shapes of objects.
- The colour of the opaque object does not affect the colour of the shadow.
- All the space behind the opaque object, up to some distance behind it seems to be filled with the shadow.
Rectilinear propagation: Light travels in a straight line. It is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Image formation by a plane mirror: We are able to see images through a mirror. Image formed by a mirror (flat) has following features:
- Reflected image retains the colour of the object.
- Image is erect but laterally inverted.
Lateral inversion: Right side of the object appears as left side in the image formed by a plane mirror. For example, if we show our right hand, image in the mirror will show as left hand.
In a mirror, if you see another person, surely the other person can also see you in that mirror.
Luminous: Objects that give out or emit light of their own are called luminous objects.
Mirror: A smooth shining surface, which rebounds the light back in same or in different directions is called a mirror.
Opaque objects: If an object completely stops the passage of all the light falling on it, it is an opaque object.
Pinhole camera: It is a device which forms a photograph-like image of a bright object on a screen.
Reflection of light: When a ray of light falls on a smooth and polished surface, light returns back in the same medium. It is called reflection.
Shadow: Opaque objects do not allow light to pass through them and cast dark patches behind them. These dark patches are called shadows.
Translucent objects: Some objects allow only a part of light falling on them to pass through, such objects are called translucent objects. For example, a single thin sheet of paper.
Transparent objects: Those objects which allow all the light to pass through them are called transparent objects.
Characteristics of a Shadow:
A shadow has the following three characteristics:
- It is always black, regardless of the colour of the object used to make the shadow
- It only shows the shape or outline of the object and not the details.
- The size of a shadow varies depending on the distance between the object and the source of light, and the distance between the object and the screen.
Reflection Surfaces
We say light is reflected when it bounces off a surface. Reflection of light helps us to see most of the things around us.
Reflection of light by a surface depends on the nature of the surface. A rough and bumpy surface (also called an irregular surface) reflects a parallel beam of light incident upon it in different directions (Fig. 13.5). A good example of a rough surface is bark of a tree and blanket. This kind of reflection is called diffused reflection.
A smooth surface (a highly polished surface) reflects a parallel beam of light incident upon it in one direction. (Fig. 13.6). A good example of a smooth surface is a mirror. When you stand in front of a mirror, you can see yourself in the mirror. This is called your image.
NCERT QUESTION ANSWERS AND EXCERCISES
1. Rearrange the boxes given below to make a sentence that helps us understand opaque objects.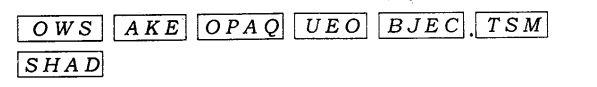
Ans:![]()
2. Classify the objects or materials given below as opaque, transparent or translucent and luminous or non-luminous:
Air, water, a piece of rock, a sheet of aluminium, a mirror, a wooden board, a sheet of polythene, a CD, smoke, a sheet of plane glass, fog, a piece of red hot iron, an umbrella, a lighted fluorescent tube, a wall, a sheet of carbon paper, the fame of a gas burner, a sheet of cardboard, a lighted torch, a sheet of cellophane, a wire mesh, kerosene stove, sun, firefly, moon.
Ans: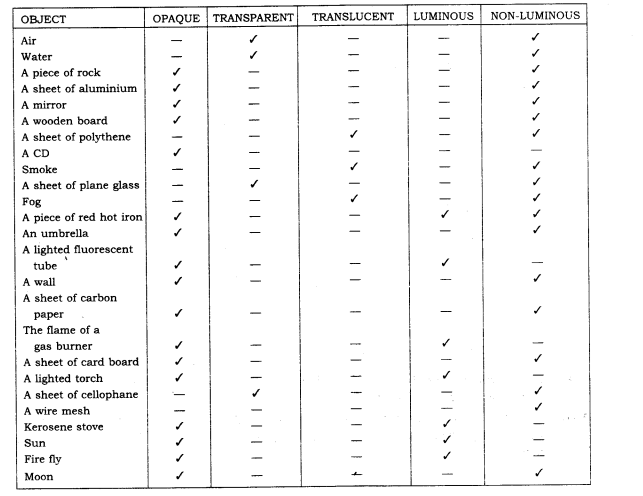
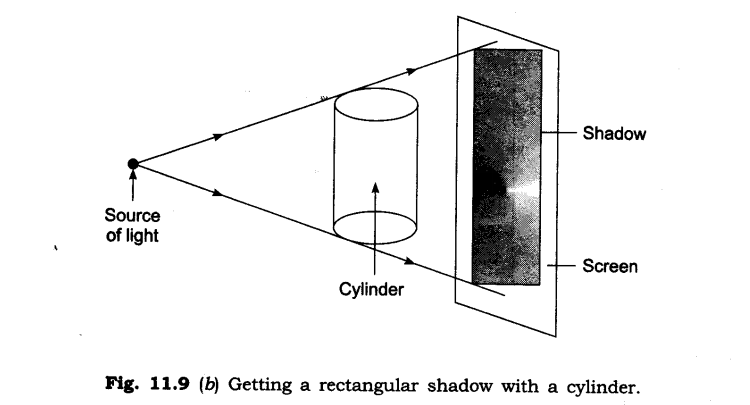
3. Can you think of creating a shape that would give a circular shadow if held in one way and a rectangular shadow if held in another way?
Ans: Yes, there are many things which give a circular shadow if held in one way and a rectangular shadow if held in another way. For example: a cylinder, a circular disc etc.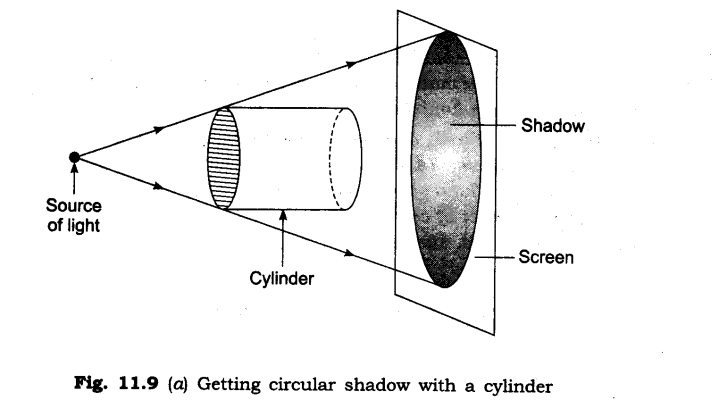
4. In a completely dark room, if you hold up a mirror in front of you, will you see a reflection of yourself in the mirror?
Ans: No, in a completely dark room no image will be formed because there is no light in the room so no reflection of light takes place and no image will be formed.





No comments:
Post a Comment