NOTES GETTING TO KNOW ABOUT PLANTS
Flowering Plants: Plants which bear flowers are called flowering plants. Their bodies are divided into roots, stem, leaves and bear flowers and fruits.
Herbs, shrubs and trees: Plants are usually grouped into herbs, shrubs and trees on the basis of their heights, stem and branches:
- (а) Herbs: Plants with green and tender stem are called herbs. They are usually short and sometimes do not have branches.
- (b) Shrubs: Some plants have branches arising from the base of the stem. The stem is hard but not very thick. They are called shrubs.
- (c) Trees: Some plants are very tall and have hard and thick stem. They have branches arising from upper part of the stem. They are called trees.

Creepers and climbers: The stem of some plants are very thin and weak. They either lie on the ground or need support to stand up. They are called creepers and climbers respectively.
Stem
- It bears leaves, buds, flowers, fruits, etc.
- The stem conducts water from the roots to the leaves and to the other parts and food from leaves to the roots and other parts of the plant.
- Potato, yams, ginger, onion, etc. though present in the soil, are actually stem and store food within them.

Leaf
- Leaves have a variety of shapes, sizes and other structures.
- Venation: The pattern of veins and veinlets on the leaves is called venation.
- Veins: Thread like structures in the leaves forming a network.

- Midrib: It is the thick vein in the middle of the leaf.
- Types of venation: Two types of venation are found:
- Reticulate: If the venation is in net like appearance on both sides of midrib, it is called reticulate. For example, peepal.
- Parallel: In the leaves of grasses, the veins and veinlets are parallel to one another. Such a venation is called parallel.
- Node: Places where leaves and branches are joined to stem are called nodes.
- Internodes: The part of stem between two nodes is called internode.


- Function of leaves
- Transpiration: It is the process of evaporation of water from the.surface of leaves.
- Photosynthesis: Green leaves synthesize food with the help of sunlight, air and water by a process called photosynthesis.
Roots
- Roots are mostly the underground part of the plant.
- They absorb water and mineral from the soil.
- They hold the soil firmly to keep the plant upright.
- Some roots store food and become plump.

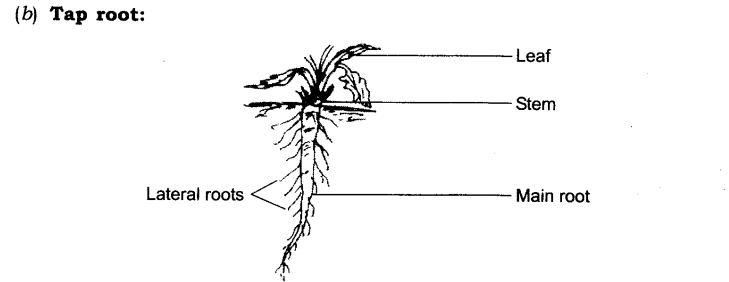
- Roots are of two types: fibrous root and taproot.

- Fibrous roots: In the plants like grass, the branches of the root come out from the base of the stem. Such roots are known as fibrous roots.
- Taproots: In some plants, the branches of the root arise from a thick structure under the ground which is called the main or primary root. Such roots are called taproots.
- Root hair: The fine hair like structures on the branches of root are root hair.
- Lateral roots: The smaller roots on taproot are called lateral roots.
- Plants having leaves with reticulate venation have taproot and plants having leaves with parallel venation have fibrous root.
Flower
- It is usually the most attractive part of a plant, also called as modified shoot
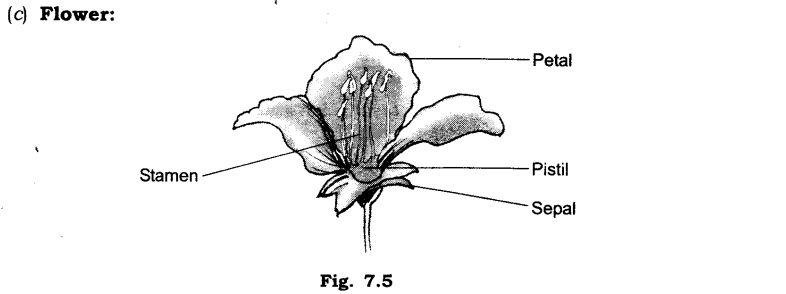
- Sepals, petals, stamens and pistils are the main parts of the flower.

- Parts of a flower are usually present in rings or whorls.
- Pedicel: The stalk that joins a flower to the plant is called the pedicel.

- Sepals: It is the outermost whorl of the flower. Often they are small, green leaf like structures. They protect the inner parts of a flower while it is still a bud.
- Petals: Inside the sepals there is the whorl of petals. Different flowers have petals of different colours. Some flowers have sweet smelling petals. With its colour and fragrance, the petals attract not only the human beings but also the insects and the birds.
- Stamens: These are 4-6 in number and are male reproductive part of a flower. Each stamen is made up of two parts—filament and anther. Anther contains pollen grains.
- Pistil: It is the innermost part of a flower. Ovary can be divided into three parts: (a) Stigma, (b) Style and (c) Ovary.
Ovary may further be divided into locules. Locules contain ovules.

Conduct: The water and minerals are transported to leaves and other parts of plant attached to the stem.
Petiole: The part of a leaf by which it is attached to the stem is called petiole. Lamina: The broad green part of leaf is called lamina.
Ovules: The small bead like structures inside the ovary are called ovules (see Fig.).
Climbers: Some plants with weak stem need support to go upright. These are called climbers.
Conduct: To carry a substance from one place to other is called to conduct. Creepers: Some plants with weak stem lie on the ground. These are called creepers. Fibrous roots: Roots in which many branches come out from the base of the stem are called fibrous roots.
Herbs: Plants with green and tender stem are called herbs.
Lamina: The broad green part of the leaf is called lamina.
Lateral roots: Smaller roots which arise from main root in the taproot systems are called lateral roots.
Midrib: The thick vein in the middle of the leaf is called the midrib.
Ovule: Small bead like structures attached in the inner wall of the ovary are called ovules.
Parallel venation: In the leaves of grass, veins are parallel to one another. This is called parallel venation.
Petal: This is the prominent part of the open flower. Different flowers have petals of different colours and of different forms.
Petiole: The part of the leaf by which it is attached to the stem is called petiole.
Photosynthesis: A process by which green plants make their food from sunlight, carbon dioxide and water is called photosynthesis.
Pistil: Innermost part of a flower is called pistil. It is female reproductive part of the flower.
Reticulate venation: When veins and veinlets form a net like design in both sides of midrib, the venation is called reticulate venation.
Sepal: Sepal protects the inner parts of flower when it is a bud.
Shrubs: Some plants have branches arising from the base of the stem to make bushy appearance. The stem is hard but not very thick. They are called shrubs.
Stamen: Stamens are the male reproductive parts of the flower.
Taproot: The root system in which a single root arises from the base of the stem, with secondary and tertiary branches is called a taproot system.
Transpiration: The loss of water in the form of vapours from the stomata on leaves is called transpiration.
Trees: Tall plants with hard, thick and woody stem are called trees.
Veins: Thread like structures in leaf are called veins.
Root Systems :
There are two main types of root systems: tap root and fibrous root system.
Tap Root System:
In the tap root system (Fig. 8.1), a single root (called the primary root) comes out from the seed after germination. Tap roots are also called true roots.
Later, smaller roots called lateral roots branch out from this primary root. Mango, neem, pine, sheesham, pea, carrot, radish, turnip, and beetroot are examples of plants in which tap roots are found.
Fibrous Root System:
Fibrous roots (Fig. 8.2), which grow from the base of the stem have a bushy appearance. These roots are thin and almost equal in size. Grass, maize, wheat, onion, sugarcane, and rice are examples of plants with fibrous roots.
Functions of Roots:
Some functions of roots are given below:
Anchoring the plant Roots help to anchor the plant firmly into the ground.
Absorption of water and nutrients from the soil They help plants to absorb water and nutrients from the soil, which are essential for their survival.
Desert plants have relatively longer roots because they penetrate deep into the soil in search of water.
Preventing soil erosion They help to bind the soil particles together, thereby preventing them from being carried away by water or wind.
Sometimes roots are modified to perform various other functions like reproduction, nutrition, etc.
Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Textbook Questions
1. Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook.
(a) Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Leaves hold the plant upright.
(c) Roots conduct water to the leaves.
(d) The number of sepals and petals in a flower is always equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are also joined together,
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal.
Ans:
(a) Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Roots hold the plant upright.
(c) Stem conducts water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and sepals in a flower is usually equal.
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are not necessarily joined together.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is not necessarily joined to the petal.
2. Draw (a) a leaf, (b) a tap root and (c) a flower, you have studied for Table 7.3 of the textbook.
Ans: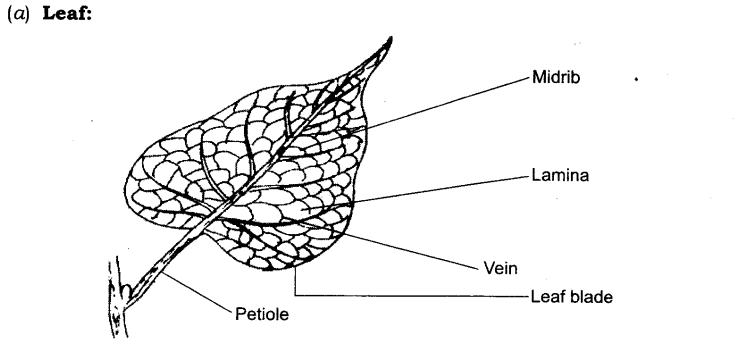
3. Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighbourhood which has a long but a weak stem? Write its name. In which category would you classify it?
Ans: Yes, we find a money plant in our house. It is a climber.
4. What is the function of a stem in a plant?
Ans: A stem performs following functions:
(i) The stem and its branches hold leaves to get maximum sunlight.
(ii) It transports water from roots to different parts of the plant.
(iii) It transports food from leaves to different parts of the plant.
(iv) It bears leaves, flowers and fruits.
5. Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation?
Wheat, tulsi, maize, grass, coriander (dhania), china rose.
Ans: Tulsi, china rose.
6. If a plant has fibrous root, what type of venation are its leaves likely to have?
Ans: Parallel venation.
7. If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Ans:Tap root.
8. Is it possible for you to recognise the leaves without seeing them? How?
Ans: We cannot exactly recognise the leaves without seeing them. We may be able to have some idea by touching and smelling them.
9. Write the names of the parts of a flower in sequence, from outside to inside.
Ans: The names of various parts of a flower from outside to inside are:
(i) Sepals
(ii) Petals
(iii) Stamens
(iv) Pistil
10. Which of the following plants have you seen? Of those that you have seen, which one have flowers?
Grass, maize, wheat, chilli, tomato, tulsi, pipal, shisham, banyan, mango, jamun, guava, pomegranate, papaya, banana, lemon, sugarcane, potato, groundnut
Ans: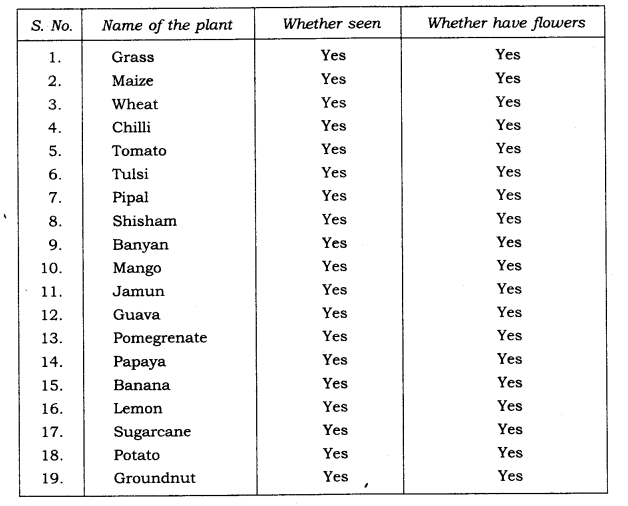
11. Name the part of the plant which produces its food. Name this process.
Ans: Leaves produce food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis.
12. In which part of a flower you are likely to find the ovary?
Ans: We find ovary in pistil. It is the lowermost part of the pistil.
13. Name two flowers, each with joined and separates sepals.
Ans:
Flowers with joined sepals:
(i) Datura
(ii) Loki
Flowers with separate sepals:
(i) Gurhal
(ii) Mustard




No comments:
Post a Comment