sample paper link
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1DmwEvm7ikwyKWYoY_8i37JHhjw4olDUG?usp=drive_link
PM
SHRI KENDRIYA VIDYALAY N.E.R. BAREILLY (2025-26)
PERIODIC
TEST -2
CLASS
–IX
SUBJECT – SCIENCE
TIME ALLOWED: 1:30 Hrs.
MAXIMUM MARKS: 40
1.
Which of the following properties does
not describe a compound?
a)
It is composed of two or more elements
b)
It is a pure substance
c)It
cannot be separated into constituents by physical method
d) it is mixed in any proportion by mass
2.
During a sprinting race, Meera suddenly felt a pull where her calf muscles
attached to
her
leg bone. Her coach explained that a specific tissue was strained, which
connects
muscles
to bones and enables movement. Which type of tissue was he referring to?
(a)
Ligament (b) Tendon (c) Cartilage (d)
Bone
3.Which
of the following quantities remains constant everywhere?
(a)
Weight (b) MASS (c) Gravitational
force d) Acceleration due to
gravity
4.
Girth of stem increases due to
a)
Apical meristem b) Intercalary
meristem c) Lateral meristem d)
vertical meristem
5..
A person standing in a moving bus that suddenly stops,the person tends to:
(a)
Fall backward (b)
Remain standing
(c)
Fall sideways (d) Fall
forward
Assertion-Reason Based Questions (1mark each)
(a)
Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A
(b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c)
A is true, but R is false.
Name
the physical quantity(d) A is false, but R is true.
6.
Assertion (A): Cardiac muscles do not get tired easily.
Reason
(R): Cardiac muscles work continuously and are resistant to fatigue
7..
Assertion: When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution placed
in a dark place the path of the beam becomes visible.
Reason: Light gets scattered by the colloidal
particles.
8.Why
are the xylem and phloem called complex tissue?
and how are the different from one other
9. Shruti walking on the road.Describe her walking in
terms of Newton's third law of motion
10.Differentiate the following activities on the basis
of voluntary or involuntary muscles with name
a) Jumping of the frog
b) pumping of the heart
c) Drawing a painting
d) Movement of chocolate in your intestine
11.Name the physical quantity that is product of mass of object and velocity.Write
its SI unit is it vector or scalar quantity ?
12.State the factors on which the gravitational force
between two objects depends.
OR
A body weighs 600 N on Earth. What would be its weight
on the Moon?
13.Differentiate between different types of muscular
tissues with diagram and also write there functions
14. State the law of gravitation given by Newton. What
is the importance of this law?
15. At Gwalior airport, Rohit has a trolley bag. He
pushes the trolley on the smooth floor of the airport. Initially, the trolley
is at rest. After applying a continuous force, the trolley begins to move and
pick up speed.
(a) Which law of motion explains why the trolley
starts moving?
(b) What is the direction of the force applied by the
boy?
(c) Name the property of the trolley that resists the
start of motion.
16. A young athlete named Raj, who is a long-distance
runner, experiences muscle soreness and fatigue after a grueling training
session. His legs feel weak and stiff, and he's unable to continue his workout.
He has also been feeling short of breath.
(a) What type of muscle tissue is primarily
responsible for Raj's leg movement, enabling him to run?
(b) Describe two main characteristics of the type of
muscle tissue that allows Raj to run long distances without fatigue.
(c) What other types of tissues are involved in Raj’s
running, and how do they work
(d) Name sweat secreting tissue.
17.a) A solution of alcohol in water has been prepared
by mixing 150 ml of alcohol with 600 ml of water. Calculate the volume.
Percentage of the solution.
b) Why? Copper sulphate solution in water does not
show Tyndall effect but mixture of water and milk shows .
(c) Suggest any one method by which we can increase
the solubility of solution
18. A stone of 1 kg is thrown with a velocity of 20
m/s across the frozen surface of the lake and
comes to rest after travelling a distance of 50 m. What is the force of
friction between the stone and ice?
MARKING SCHEME`
1.d) it is mixed in any proportion by mass
2. (b) Tendon
3. (b) mass
4.c lateral meristem.
5. (d) Fall forward
6.a
7.a
8.Xylem and phloem are called complex tissues because
they are each composed of more than one type of cell that work together to perform a specific, unified function.
(b) The direction of the force applied by the boy is in the same direction in which the trolley moves (forward, along the push).
(c) The property of the trolley that resists the start of motion is inertia of rest.
16.(a) The muscle tissue responsible for Raj’s leg movement while running is skeletal (voluntary, striated) muscle tissue.
(b) Two main characteristics of skeletal muscle that help in long-distance running:
Contractile & Voluntary: They contract and relax under Raj’s conscious control, producing movement of the legs.
Rich in Mitochondria (especially in red muscle fibers): They provide a continuous supply of energy (ATP) through aerobic respiration, helping Raj sustain running for long periods.
(c) Other tissues involved in running and their roles:
Nervous tissue: Sends signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles, coordinating movement.
Connective tissue (bones, ligaments, tendons, cartilage): Bones act as levers, tendons attach muscles to bones, and ligaments hold joints in place.
Epithelial tissue (lungs & blood vessels): Helps in oxygen exchange (lungs) and regulates blood flow.
Blood (connective tissue): Transports oxygen and nutrients to muscles and removes waste like carbon dioxide and lactic acid.
(d) The sweat-secreting tissue is epithelial tissue of sweat glands (specifically, glandular epithelium).
17.a
Given:
Volume of alcohol (solute) = 150 ml
Volume of water (solvent) = 600 ml
Total volume of solution = 150+600=750ml
Now calculate:
Volume percentage of alcohol=750150×100When temperature rises, solvent molecules gain more kinetic energy.
This allows them to break solute particles apart more easily and dissolve more solute.
✅ Example: More sugar dissolves in hot water than in cold water.
18.Given data:
Mass of stone,
Initial velocity,
Final velocity,
Distance travelled,
Substitute values:
(Negative sign shows retardation due to friction.)
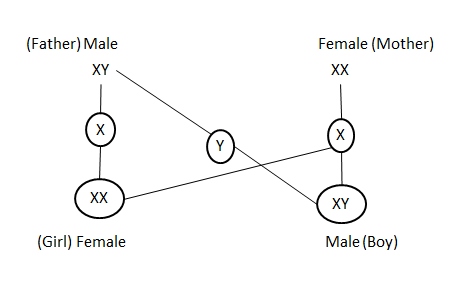
Heredity-The transmission of characters from the parents to their off spring is called heredity.The hereditary information is present in the sex cells or in gametes of the parents.
The hereditary information is present in the sex cells (or gametes) of the parents. Thus, gametes constitute the link between one generation and the next, and pass on the paternal [father's] and maternal [mother's] character (or traits) to the offspring.
The relation that continues to exist between successive generations is referred to as Heredity.
If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and a trait B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?
Answer
Asexually reproducing species show very few variations which are seen usually due to mutation. Any such variation in an individual takes time to become considerable part of the population as it shows up only in individual's progeny. Therefore, if a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species, it must be a recent variation and if a trait B exists in 60% of the same population, it is likely to have arisen earlier.
How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer
Any species is adapted to survive in a particular niche. In case of any sudden change in that niche the species may not survive if all the individuals are alike. But if few individuals are different due to variations they can adapt to the changed conditions and thus species can avoid being wiped out. Therefore, the creation of variations in a species promote its evolution and hence its survival.
How do Mendel's experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer
Mendel used a number of contrasting visible characters of garden peas – round/wrinkled seeds, tall/short plants, white/violet flowers and so on. When he crossed plants with contrasting characters, there were no halfway characteristics in the first generation. For example, if a tall plant was crossed with a short plant, all plants were either tall or short and no plant was found with medium height. In F2 generation cross between two tall plants gave short plant as well. This proved that there are two contrasting characters out of which one is dominant which masks the effect of other which is recessive.
How do Mendel's experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer
Mendel crossed a tall pea plant with round seeds with a short pea plant with wrinkled seeds. The F1 progeny were all tall with round seeds. Thus, tallness and round seeds are the dominant traits.
Mendel then used F1 progeny to generate F2 progeny by self-pollination. He observed that some F2 progeny were tall plants with round seeds, and some were short plants with wrinkled seeds. However, he also found that some F2 progeny showed new combinations like tall but with wrinkled seeds, while others would be short but have round seeds. Thus, Mendel’s experiments showed that traits are inherited independently.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits – blood group A or O – is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer
No, the given information is not sufficient to tell which of the traits is dominant because we don't know all possible blood groups of all the progeny.
The father's blood group is A, which means he can be homozygous (AA) or heterozygous (AO). Similarly, mother can also be homozygous or heterozygous.
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as
Answer
TtWW
Reason — Possibility of genotype for parent plants:
Since, the progeny all bore violet flowers, the tall parent must be homozygous for violet flower colour i.e. WW. Also, almost half of the progeny were short shows that the tall parent must be heterozygous for tallness i.e. Tt. Therefore, the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as TtWW.
A study found that children with light-coloured eyes are likely to have parents with light-coloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
Answer
No, we cannot say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive based on above given fact because:
Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
Answer
Following are the steps that should be followed in order to find the dominant coat colour in dogs:
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny?
Answer
During gamete formation the cell divides by meiosis giving four haploid (n) cells. The normal number of chromosomes in human a cell is 46 i.e. 23 pairs. The gamete cells, therefore, formed after meiosis have 23 chromosomes each. When fertilization occurs, the male gamete and female gamete fuse together and the original number of chromosomes is restored. This means that the zygote has 46 (23+23) chromosomes — 23 from male gamete and 23 from female gamete. This is how the equal genetic
PM SHRI KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA N.E.R BAREILLY
PERIODIC TEST – 2
SESSION – 2025-26
CLASS – 10th SUBJECT
– SCIENCE
TIME – 11/2HRS MM – 40
|
Q.No |
Section
A |
Marks |
|
1 |
Which of the following is a correct combination of function and
part of the brain? A. Posture and balance: Cerebrum B. Salivation: Medulla in midbrain C. Hunger: Pons in hindbrain D. Blood pressure: Medulla in hindbrain |
1 |
|
2 |
The
blood glucose level in a patient was very high. It may be due to inadequate
secretion of: A. growth hormone from pituitary gland B. oestrogen from ovary C.
insulin from pituitary gland D.
insulin from pancreas |
1 |
|
3 |
Which of the following substances when
dissolved in equal volume of water, will have the highest pH value? A. Sulphuric acid B. Acetic acid C. Magnesium hydroxide D.
Sodium hydroxide |
1 |
|
4 |
An electric iron of resistance 20 Ω draws a
current of 5 A. The heat developed in the iron in 30 seconds is:- a)15000J b)6000J c)1500J d)3000j |
1 |
|
5 |
The atomic no. of three elements X,Y& Z are 19 ,13 and
17 respectively.which of the following statement about these elements is
correct? A.X is a metal and it forms basic oxide. B.Y is a non metal and it forms acidic oxides C.Both Y and Z are non metals . D. X is a non metal while Z is a metal. |
1 |
|
6 |
There is a cerebellar dysfunction in a patient. Which of the
following activities will get disturbed in this patient as a result of this? A. Salivation. B. Hunger
control. C. Posture and balance D. Regulation of B.P. |
1 |
|
7 |
The oxide which can react with HCl as well KOH to give
corresponding salt and water is. A. CuO B.Al2O3 C.Na2O D.K2O. |
1 |
|
8 |
The following question consists of two statements – Assertion
(A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate
option given below: A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct
explanation of A. B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct
explanation of A. C. A is true but R is false. D. A is false but R is true Assertion-receptors are usually
located in our sense organs and perceive a particular stimulus. Reason- different sense
organs have different receptors for detecting stimuli. |
1 |
|
|
Section
B |
|
|
9 |
|
2 |
|
10 |
What are reflex actions. Draw a well labelled reflex arc. |
2 |
|
11 |
|
2 |
|
12 |
Show the formation of i) CaO ii)MgO |
2 |
|
|
Section C |
|
|
13 |
|
3 |
|
14 |
|
3 |
|
|
Section D |
|
|
15 |
Oxygen can combine with both metals and non-metals. It combines with
Calcium to form CaO and with carbon to form CO2. (a) What type of bond is formed between carbon and oxygen? (b) Identify the type of bond formed between Calcium and oxygen. (c)
Which of the above compounds will be a good conductor of electricity in
molten state and why? (d) Comment on the physical state (solid, liquid or gas) of CaO and
CO2. (e) What is the valency of
carbon in CO2? |
5 |
|
16 |
ii)Name and define the physical quantity
defined by the slope of V-I Curve given in the diagram. Use this graph to
find the value of this physical quantity in SI units. iii)Establish relationship between 1kWh and
1 joule. |
5 |
|
|
Section E |
|
|
17 |
Mohan and Rohit observed that shoots of a plant growing
in shade bend towards the sunlight. Whereas, leaves of ‘Touch me not’ plant
fold and droop soon after touching. They were curious to know how these
movements occur in plants |
4 |
|
18 |
The
extraction of metals from their ores and refining them for the use is known
as metallurgy. It Involves several steps such as concentration of ore into
oxide through calcination or roasting,
reduction of oxides using suitable reducing agents and refining of metals. i)Name an ore of mercury. ii)write a chemical equation for the
calcination of ZnCO3. iii) write the difference between roasting
and calcination. |
2+2 |
B. No, aluminium wire will not melt because metals have high melting points.
10.A reflex action is a quick, automatic, and involuntary response to a stimulus that occurs without conscious thought, often to protect the body from harm.
(ii)𝐼= 𝑉/𝑅 =8/(4+4)=1 𝐴
12.
(i) No, ‘X’ is highly reactive and will catch fire.
(ii) Sodium.
It is extracted from molten sodium chloride by electrolytic reduction
Cathode: Na+ + e- ---- Na
Anode: 2Cl- Cl2 + 2e-
(Potassium is also a correct option)
OR
B.
(i) Copper gets oxidised/corroded to basic copper carbonate which is greenish in colour.
(ii) No, iron will rust and the reddish layer of rust will come off exposing iron to air, the dome will not be stable. Copper on the other hand on corrosion forms a protective layer which does not allow further corrosion.
(iii) Copper is a highly malleable metal, its thin sheets can be used to give different shapes of roofs, like the shape of a dome.
14.A.
(i) X = NaHCO3; Z = Na2CO3 (0.5+0.5)
(ii) Decomposition reaction (0.5)
(iii) Solution A (0.5)
(iv)Increasing order or H+ ions C<B<A (1)
OR
B.
(i) As bee sting is acidic and wasp sting is basic. (1)
(ii) To change the nature of soil to (neutral or basic). (1)
(iii) To protect sculptures from the effects of certain gases present in
environment and acid rain. (1)
15.(a) Covalent bond (b) Ionic bond (c) CaO, due to presence of free ions in molten state. (d) CaO is solid while CO2 is a gas. (e) 4
16.i) Ohm's Law is the law, which states that the electric current (I) flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage (V) applied across it and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. Mathematically, it can be represented as: (1)
V=IR
ii.The slope of the VI curve indicates the resistance (R) in ohms (Ω), as per Ohm's Law which states that V = IR.
From the graph, select two points. For example, the point (0,0) and (0.8, 6) gives ΔV = 6 - 0 = 6 V and ΔI = 0.8 - 0 = 0.8 A
Calculate the slope: R = 6 V / 0.8 A = 7.5 Ω.
iii.) 1kWh=3,600,000 j
17.
A. ● Bending of shoots of plants is a response to the stimulus and a directional, growth-related movement.
● When growing plants detect sunlight, a hormone called auxin, synthesized at shoot tip helps the cells to grow longer.
● When light is coming from one side of the plant, auxin diffuses to the shady side of the shoot.
● This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells of the shoot to grow 4 longer on the side of the shoot which is away from the light. Thus, plant appears to bend towards light. (0.5 x 4 =2)
OR
B. ● Leaves of ‘Touch me not’ plant respond to the stimulus by showing growth independent movement.
● These plants use electrical–chemical means to convey the information from cell to cell.
Movement happens at a point different from the point of touch.
● Plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them, resulting in swelling or shrinking, and therefore in changing shape. (0.5 x 4 =2)
C. Growth of pollen tubes towards the ovule is an example of chemotropism whereas bending of shoots towards sunlight is an example of phototropism. (1)
D. i) Although both plants and animals show electrical–chemical means to convey the information from cell to cell but unlike nerve cells in animals there is no specialized tissue in plants for conduction of information. (0.5)
ii) In animal cells, change in shape occurs because of the specialized proteins found in muscle cells; plant cells change shape by changing the amount of water in them. (0.5)
18.i cinnebar.
ii.Zinc carbonate is heated strongly in limited supply of air to convert it to oxide. This process is called calcination.
sample paper link https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1DmwEvm7ikwyKWYoY_8i37JHhjw4olDUG?usp=drive_link